upgrade karpenter
Announcement
⚠️ This is a Karpenter Helm chart upgrade guide for v0.26.0 to v0.26.1, which are now deprecated. Use this only as a reference.
Overview
This guide shows how to upgrade Karpenter from v0.26.0 to v0.26.1 on an EKS cluster using Helm.
Important notes
This guide assumes you already have an older version of Karpenter installed on your EKS cluster.
This is not a fresh install. We are upgrading from Karpenter v0.26.0 to v0.26.1.
Background
Karpenter
Karpenter is an open source cluster autoscaler. It detects pods that cannot be scheduled and creates new nodes automatically.
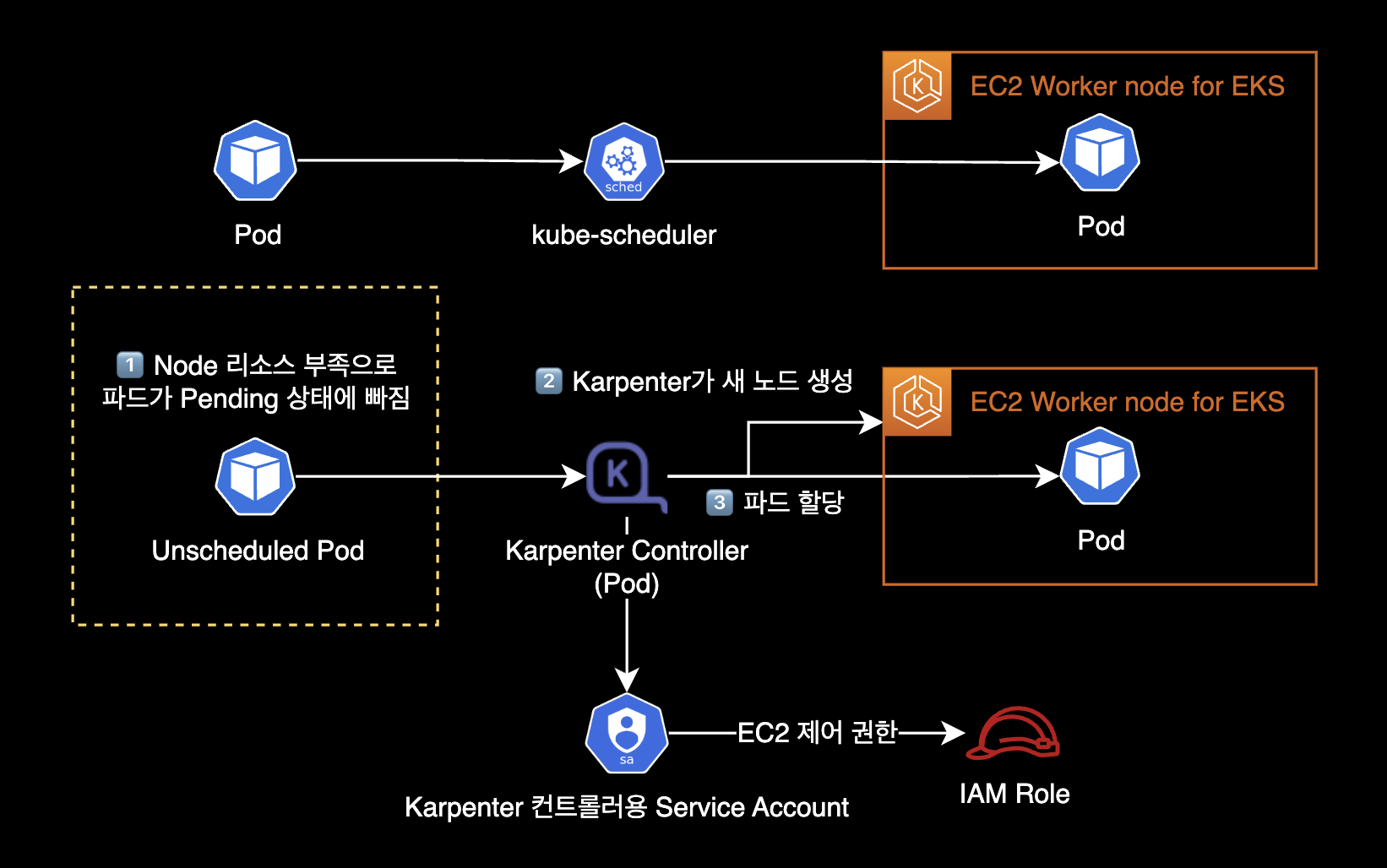
Unlike Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler which uses ASGAuto Scaling Group, Karpenter Controller (Pod) creates and deletes EC2 instances directly.
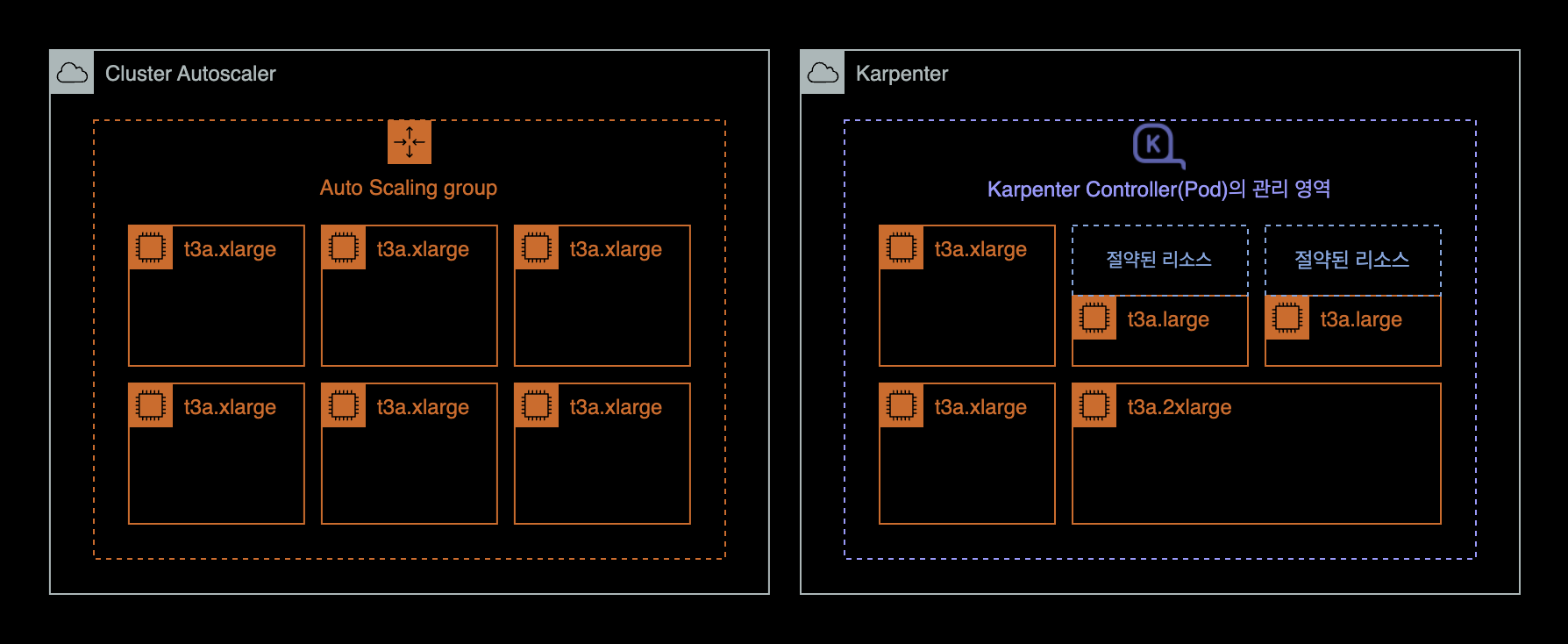
Here are the benefits of Karpenter:
- Karpenter manages instances directly without ASG. This makes node creation and deletion faster.
- Karpenter does not use node groups or auto scaling groups. This makes cluster node management easier.
- Karpenter calculates CPU and memory needs for pending pods. It picks the right mix of instance types. This saves EC2 costs and allows flexible scaling.
Karpenter charts
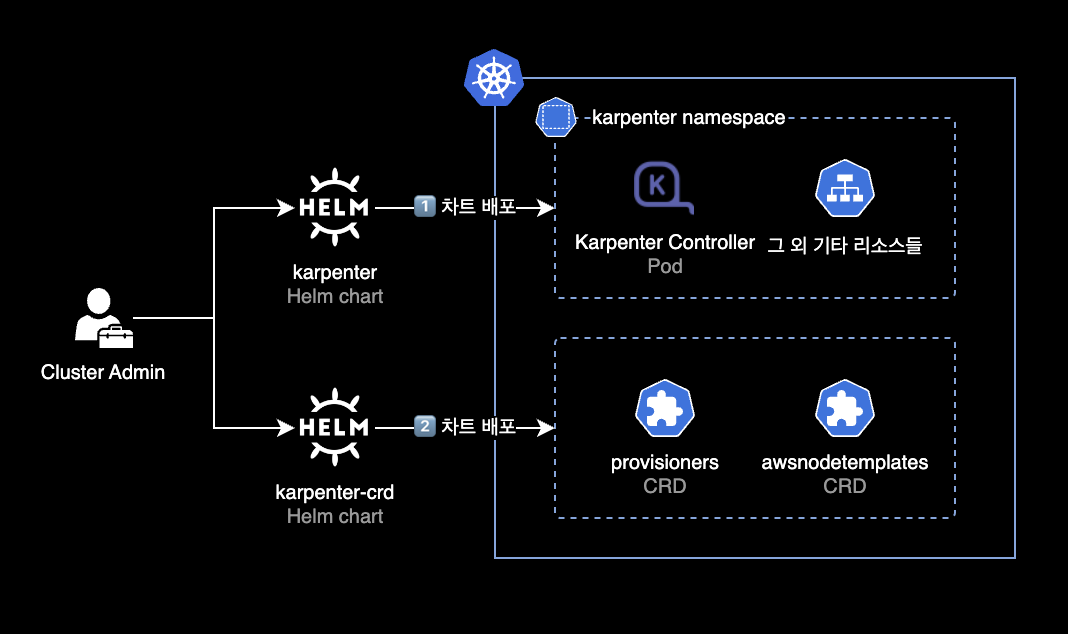
Helm chart is the recommended way to install Karpenter in most cases. Karpenter uses two Helm charts:
- karpenter: Karpenter Controller. Deployed via Helm chart.
- karpenter-crd: Karpenter CRDs. Deployed via Helm chart.
After deploying both charts, you need to create provisioners and awsnodetemplates resources using kubectl apply. The Karpenter Controller uses these resources.
Environment
Cluster environment
- EKS v1.24
- Node CPU architecture: AMD64 (x86_64)
- Karpenter: v0.26.0 → v0.26.1
- Install and upgrade via Helm chart
- Karpenter CRD also upgrades from v0.26.0 to v0.26.1
Local environment
- OS: macOS 13.2.1 (Ventura)
- Helm: v3.11.1
Upgrade steps
1. Set environment variable
Set the Karpenter version in your terminal.
KARPENTER_VERSION=v0.26.1You can find all versions on the Karpenter Github Releases page.
2. Install Karpenter Controller
Write Karpenter Controller values
This guide assumes you have an older Karpenter Helm chart already deployed on your cluster.
You need IAM roles for the Karpenter Controller and Instance Profile for nodes. See the Karpenter initial install guide for setup steps.
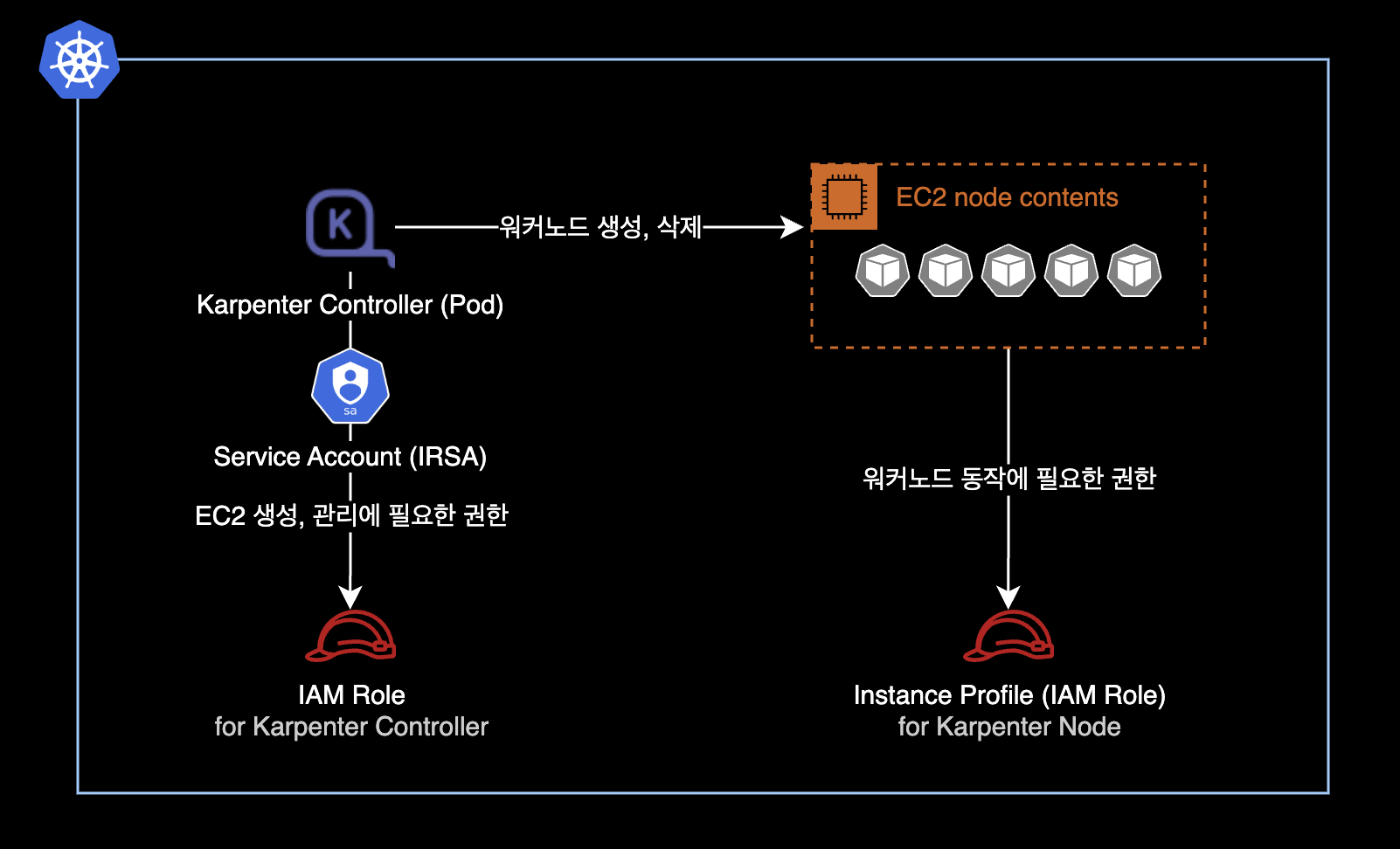
- Creating IAM roles is outside the scope of this guide.
Download chart (optional)
To check the default values file or template structure, download the chart locally with helm pull. Use --untar to get the chart directory instead of a .tgz file.
helm pull oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter \
--version ${KARPENTER_VERSION} \
--untarAfter download, you will see a karpenter/ directory. Inside, you can check the values.yaml file and template structure.
values.yaml example
I wrote a values.yaml file for the Karpenter Controller. This deploys Karpenter version v0.26.1.
# -- Overrides the chart's name.
nameOverride: ""
# -- Overrides the chart's computed fullname.
fullnameOverride: ""
# -- Additional labels to add into metadata.
additionalLabels: {
app: karpenter
}
# -- Additional annotations to add into metadata.
additionalAnnotations: {}
# -- Image pull policy for Docker images.
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# -- Image pull secrets for Docker images.
imagePullSecrets: []
serviceAccount:
# -- Specifies if a ServiceAccount should be created.
create: true
# -- The name of the ServiceAccount to use.
# If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template.
name: "karpenter"
# -- Additional annotations for the ServiceAccount.
annotations: {
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/KarpenterControllerRole-<YOUR_CLUSTER_NAME_HERE>"
}
# -- Specifies additional rules for the core ClusterRole.
additionalClusterRoleRules: []
serviceMonitor:
# -- Specifies whether a ServiceMonitor should be created.
enabled: false
# -- Additional labels for the ServiceMonitor.
additionalLabels: {}
# -- Endpoint configuration for the ServiceMonitor.
endpointConfig: {}
# -- Number of replicas.
replicas: 2
# -- The number of old ReplicaSets to retain to allow rollback.
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
# -- Strategy for updating the pod.
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
# -- Additional labels for the pod.
podLabels: {}
# -- Additional annotations for the pod.
podAnnotations: {}
podDisruptionBudget:
name: karpenter
maxUnavailable: 1
# -- SecurityContext for the pod.
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
# -- PriorityClass name for the pod.
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
# -- Override the default termination grace period for the pod.
terminationGracePeriodSeconds:
# -- Bind the pod to the host network.
# This is required when using a custom CNI.
hostNetwork: false
# -- Configure the DNS Policy for the pod
dnsPolicy: Default
# -- Configure DNS Config for the pod
dnsConfig: {}
# options:
# - name: ndots
# value: "1"
# -- Node selectors to schedule the pod to nodes with labels.
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
# -- Affinity rules for scheduling the pod.
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: karpenter.sh/provisioner-name
operator: DoesNotExist
- matchExpressions:
- key: eks.amazonaws.com/nodegroup
operator: In
values:
# Deploy Karpenter Controller (Pod) to existing node group via nodeAffinity
- <YOUR_NODEGROUP_NAME_HERE>
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app.kubernetes.io/instance
operator: In
values:
- karpenter
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
# -- topologySpreadConstraints to increase the controller resilience
topologySpreadConstraints:
- maxSkew: 1
topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone
whenUnsatisfiable: ScheduleAnyway
# -- Tolerations to allow the pod to be scheduled to nodes with taints.
tolerations:
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
# -- Additional volumes for the pod.
extraVolumes: []
# - name: aws-iam-token
# projected:
# defaultMode: 420
# sources:
# - serviceAccountToken:
# audience: sts.amazonaws.com
# expirationSeconds: 86400
# path: token
# -- Array of extra K8s manifests to deploy
extraObjects: []
#- apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
# kind: AWSNodeTemplate
# metadata:
# name: default
# spec:
# subnetSelector:
# karpenter.sh/discovery: {CLUSTER_NAME}
# securityGroupSelector:
# karpenter.sh/discovery: {CLUSTER_NAME}
controller:
image:
# -- Repository path to the controller image.
repository: public.ecr.aws/karpenter/controller
# -- Tag of the controller image.
tag: v0.26.1
# -- SHA256 digest of the controller image.
digest: sha256:5dfe506624961f386b68556dd1cc850bfe3a42b62d2dd5dcb8b21d1a89ec817c
# -- SecurityContext for the controller container.
securityContext: {}
# -- Additional environment variables for the controller pod.
env: []
# - name: AWS_REGION
# value: eu-west-1
envFrom: []
# -- Resources for the controller pod.
resources: {}
# We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious
# choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little
# resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following
# lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.
# requests:
# cpu: 1
# memory: 1Gi
# limits:
# cpu: 1
# memory: 1Gi
# -- Controller outputPaths - default to stdout only
outputPaths:
- stdout
# -- Controller errorOutputPaths - default to stderr only
errorOutputPaths:
- stderr
# -- Controller log level, defaults to the global log level
logLevel: ""
# -- Controller log encoding, defaults to the global log encoding
logEncoding: ""
# -- Additional volumeMounts for the controller pod.
extraVolumeMounts: []
# - name: aws-iam-token
# mountPath: /var/run/secrets/eks.amazonaws.com/serviceaccount
# readOnly: true
# -- Additional sidecarContainer config
sidecarContainer: []
# -- Additional volumeMounts for the sidecar - this will be added to the volume mounts on top of extraVolumeMounts
sidecarVolumeMounts: []
metrics:
# -- The container port to use for metrics.
port: 8080
healthProbe:
# -- The container port to use for http health probe.
port: 8081
webhook:
logLevel: error
# -- The container port to use for the webhook.
port: 8443
# -- Global log level
logLevel: debug
# -- Gloabl log encoding
logEncoding: console
# -- Global Settings to configure Karpenter
settings:
# -- The maximum length of a batch window. The longer this is, the more pods we can consider for provisioning at one
# time which usually results in fewer but larger nodes.
batchMaxDuration: 10s
# -- The maximum amount of time with no new ending pods that if exceeded ends the current batching window. If pods arrive
# faster than this time, the batching window will be extended up to the maxDuration. If they arrive slower, the pods
# will be batched separately.
batchIdleDuration: 1s
# -- AWS-specific configuration values
aws:
# -- Cluster name.
clusterName: "<YOUR_CLUSTER_NAME>"
# -- Cluster endpoint. If not set, will be discovered during startup (EKS only)
clusterEndpoint: ""
# -- The default instance profile to use when launching nodes
defaultInstanceProfile: "KarpenterNodeInstanceProfile-<YOUR_CLUSTER_NAME_HERE>"
# -- If true then instances that support pod ENI will report a vpc.amazonaws.com/pod-eni resource
enablePodENI: false
# -- Indicates whether new nodes should use ENI-based pod density
# DEPRECATED: Use `.spec.kubeletConfiguration.maxPods` to set pod density on a per-provisioner basis
enableENILimitedPodDensity: true
# -- If true then assume we can't reach AWS services which don't have a VPC endpoint
# This also has the effect of disabling look-ups to the AWS pricing endpoint
isolatedVPC: false
# -- The node naming convention (either "ip-name" or "resource-name")
nodeNameConvention: "ip-name"
# -- The VM memory overhead as a percent that will be subtracted from the total memory for all instance types
vmMemoryOverheadPercent: 0.075
# -- interruptionQueueName is disabled if not specified. Enabling interruption handling may
# require additional permissions on the controller service account. Additional permissions are outlined in the docs.
interruptionQueueName: ""
# -- The global tags to use on all AWS infrastructure resources (launch templates, instances, etc.) across node templates
tags:
Creator: "younsung.lee@company.com"
ManagedBy: "Helm"
Maintainer: "younsung.lee@company.com"
This values.yaml is based on the official values.yaml from the Karpenter Github repo.
Deploy Karpenter Controller with Helm
Install the Karpenter Controller using Helm.
This command works for both fresh installs and version upgrades.
$ helm upgrade \
--install \
--namespace karpenter \
--create-namespace \
karpenter oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter \
--version ${KARPENTER_VERSION} \
--values values.yaml \
--waitPulled: public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter:v0.26.1
Digest: sha256:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Release "karpenter" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: karpenter
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Mar 6 21:47:08 2023
NAMESPACE: karpenter
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 5
TEST SUITE: NoneIf you see deployed status, the deployment was successful.
Check the current status of the Karpenter Controller.
$ kubectl get pod \
-n karpenter \
-o wideNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
karpenter-7b6b6f6bfd-t2zvh 1/1 Running 0 10m xx.xxx.xxx.14 ip-xx-xxx-xxx-236.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
karpenter-7b6b6f6bfd-xkc9q 1/1 Running 0 10m xx.xxx.xxx.196 ip-xx-xxx-xxx-176.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>By default, the Helm chart deploys 2 Karpenter Controller pods.
Check the recent logs of the Karpenter Controller pods.
$ kubectl logs -f \
-n karpenter \
-c controller \
-l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter3. Install Karpenter CRDs
Install the CRD chart for the Karpenter Controller.
This command works for both fresh installs and version upgrades.
$ helm upgrade \
--install \
--namespace karpenter \
--create-namespace \
karpenter-crd oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter-crd \
--version ${KARPENTER_VERSION} \
--waitRelease "karpenter" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
Pulled: public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter-crd:v0.26.1
Digest: sha256:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
NAME: karpenter-crd
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Mar 6 21:03:51 2023
NAMESPACE: karpenter
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: NoneIf you see deployed status, the deployment was successful.
4. Check chart results
Check the chart info and deployment status for karpenter and karpenter-crd.
$ helm list -n karpenterNAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
karpenter karpenter 5 2023-03-06 21:47:08.187374 +0900 KST deployed karpenter-v0.26.1 0.26.1
karpenter-crd karpenter 2 2023-03-06 21:03:51.831199 +0900 KST deployed karpenter-crd-v0.26.1 0.26.1Both Karpenter Controller and CRD are deployed at version v0.26.1.
5. Create CRDs
Check the CRD creation results.
$ kubectl api-resources \
--categories karpenter \
-o wideNAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND VERBS CATEGORIES
awsnodetemplates karpenter.k8s.aws/v1alpha1 false AWSNodeTemplate delete,deletecollection,get,list,patch,create,update,watch karpenter
provisioners karpenter.sh/v1alpha5 false Provisioner delete,deletecollection,get,list,patch,create,update,watch karpenterYou can see provisioners and awsnodetemplates CRDs are in use.
The Karpenter Controller Pod uses these 2 CRDs to provision new EC2 nodes:
- provisioners: Instance types, kubelet parameters, consolidationauto cleanup of unused nodes settings, etc.
- awsnodetemplates: AMI, subnet, security group settings, etc.
crds.yaml example
Create a crds.yaml file to set up the default CRDs.
cat << EOF > crds.yaml
---
# Reference:
# https://karpenter.sh/v0.26.1/concepts/provisioners/
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5
kind: Provisioner
metadata:
name: default
labels:
app: karpenter
version: v0.26.1
maintainer: younsung.lee
spec:
# Enables consolidation which attempts to reduce cluster cost by both removing un-needed nodes and down-sizing those
# that can't be removed. Mutually exclusive with the ttlSecondsAfterEmpty parameter.
consolidation:
enabled: true
# If omitted, the feature is disabled and nodes will never expire. If set to less time than it requires for a node
# to become ready, the node may expire before any pods successfully start.
ttlSecondsUntilExpired: 1209600 # 14 Days = 60 * 60 * 24 * 14 Seconds;
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["on-demand"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-family
operator: In
values: ["t3a"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-size
operator: In
values: ["nano", "micro", "small", "medium", "large", "xlarge"]
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values: ["linux"]
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values: ["amd64"]
- key: topology.kubernetes.io/zone
operator: In
values: ["ap-northeast-2a", "ap-northeast-2c"]
providerRef:
name: default
---
# Reference:
# https://karpenter.sh/v0.26.1/concepts/node-templates/
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: AWSNodeTemplate
metadata:
name: default
labels:
app: karpenter
version: v0.26.1
maintainer: younsung.lee
spec:
amiFamily: AL2
subnetSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: <YOUR_CLUSTER_NAME_HERE>
securityGroupSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: <YOUR_CLUSTER_NAME_HERE>
EOFCreate provisioners and awsnodetemplates in the EKS cluster.
$ kubectl apply -f crds.yamlprovisioner.karpenter.sh/default created
awsnodetemplate.karpenter.k8s.aws/default createdThe provisioners and awsnodetemplates resources are created. Note that these resources are cluster-scoped, not namespace-scoped.
You can list the current Karpenter CRDs with kubectl get.
$ kubectl get provisioners,awsnodetemplatesNAME AGE
provisioner.karpenter.sh/default 68m
NAME AGE
awsnodetemplate.karpenter.k8s.aws/default 68m6. Monitoring
Monitor Karpenter Controller logs
Monitor the Karpenter Controller logs for at least 10 minutes.
$ kubectl logs -f \
-n karpenter \
-c controller \
-l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenterIn normal situations, you will only see DEBUG and INFO level logs.
If you see ERROR level logs repeatedly, there may be IAM permission issues or config errors. Fix these issues for the Karpenter Controller to work properly.
Monitor node status
Also monitor the overall worker node status.
$ kubectl get node -L beta.kubernetes.io/instance-typeNAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INSTANCE-TYPE
ip-xx-xxx-xxx-132.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 13m v1.24.10-eks-48e63af t3a.medium
ip-xx-xxx-xxx-176.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 4d4h v1.24.9-eks-49d8fe8 t3a.medium
ip-xx-xxx-xxx-171.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 13m v1.24.10-eks-48e63af t3a.xlarge
ip-xx-xxx-xxx-236.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 4d4h v1.24.9-eks-49d8fe8 t3a.mediumResult
Karpenter upgrade from v0.26.0 to v0.26.1 is complete.
$ helm list -n karpenterNAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
karpenter karpenter 5 2023-03-06 21:47:08.187374 +0900 KST deployed karpenter-v0.26.1 0.26.1
karpenter-crd karpenter 2 2023-03-06 21:03:51.831199 +0900 KST deployed karpenter-crd-v0.26.1 0.26.1References
- Karpenter v0.26.1 Upgrade Guide: Official Karpenter docs
- Github - Karpenter:
karpenterchart - Github - Karpenter CRD:
karpenter-crdchart